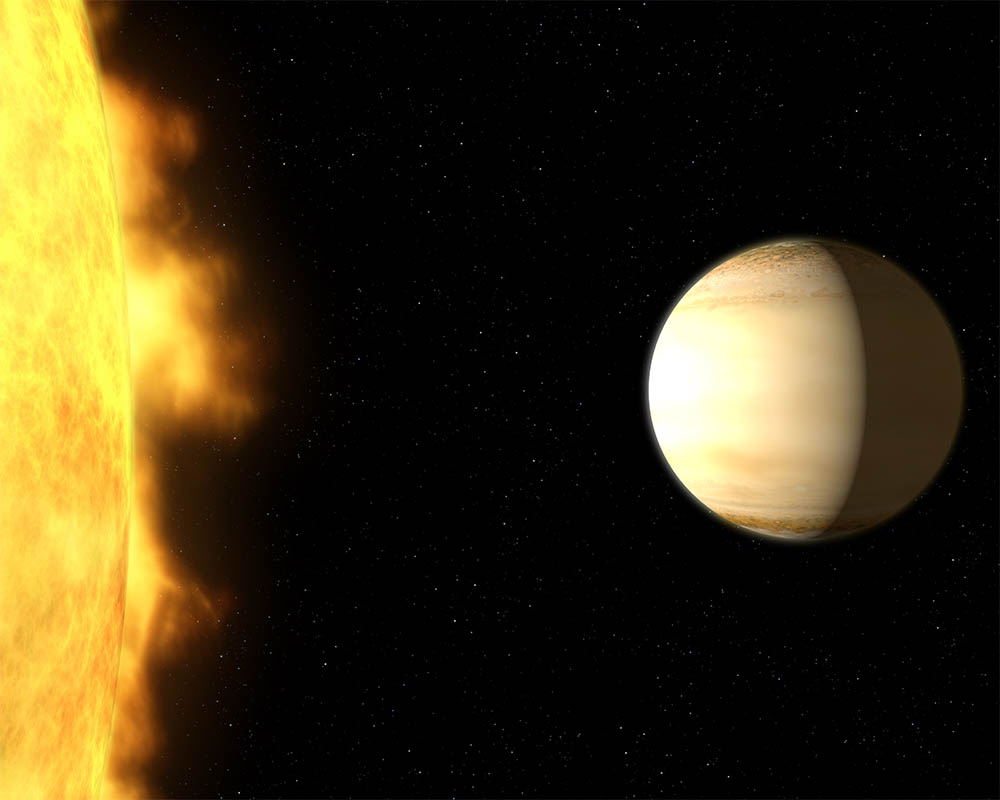
Using Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, scientists studied the “hot Saturn” called WASP-39b – a hot, bloated, Saturn-mass exoplanet located about 700 light-years from Earth. By dissecting starlight filtering through the planet’s atmosphere into its component colors, the team found clear evidence for a large amount of water vapor. (NASA, ESA, G. Bacon and A. Feild (STScI), and H. Wakeford (STScI/Univ. of Exeter))
Home Using Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, scientists studied the “hot Saturn” called WASP-39b – a hot, bloated, Saturn-mass exoplanet located about 700 light-years from Earth. By dissecting starlight filtering through the planet’s atmosphere into its component colors, the team found clear evidence for a large amount of water vapor. (NASA, ESA, G. Bacon and A. Feild (STScI), and H. Wakeford (STScI/Univ. of Exeter)) Using Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, scientists studied the "hot Saturn" called WASP-39b - a hot, bloated, Saturn-mass exoplanet located about 700 light-years from Earth. By dissecting starlight filtering through the planet's atmosphere into its component colors, the team found clear evidence for a large amount of water vapor. (NASA, ESA, G. Bacon and A. Feild (STScI), and H. Wakeford (STScI/Univ. of Exeter))
Using Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, scientists studied the “hot Saturn” called WASP-39b – a hot, bloated, Saturn-mass exoplanet located about 700 light-years from Earth. By dissecting starlight filtering through the planet’s atmosphere into its component colors, the team found clear evidence for a large amount of water vapor. (NASA, ESA, G. Bacon and A. Feild (STScI), and H. Wakeford (STScI/Univ. of Exeter))