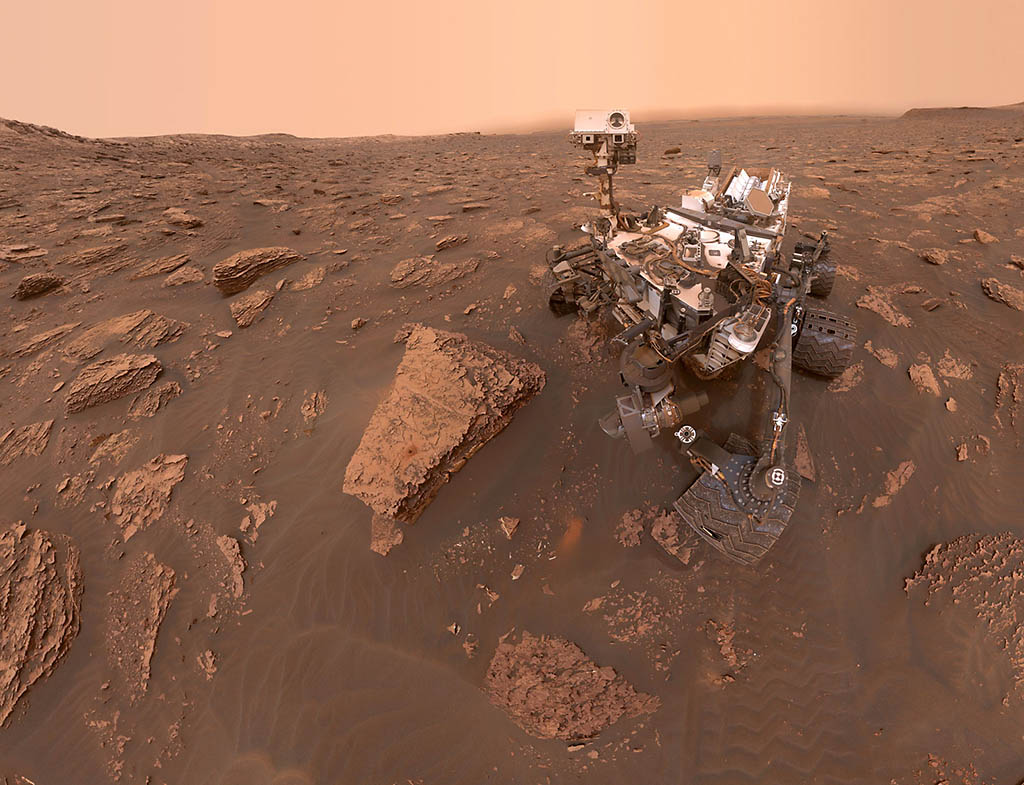
A self-portrait taken by NASA’s Curiosity rover taken on Sol 2082 (June 15, 2018). A Martian dust storm has reduced sunlight and visibility at the rover’s location in Gale Crater. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)
Home A self-portrait taken by NASA’s Curiosity rover taken on Sol 2082 (June 15, 2018). A Martian dust storm has reduced sunlight and visibility at the rover’s location in Gale Crater. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS) A self-portrait taken by NASA's Curiosity rover taken on Sol 2082 (June 15, 2018). A Martian dust storm has reduced sunlight and visibility at the rover's location in Gale Crater. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)