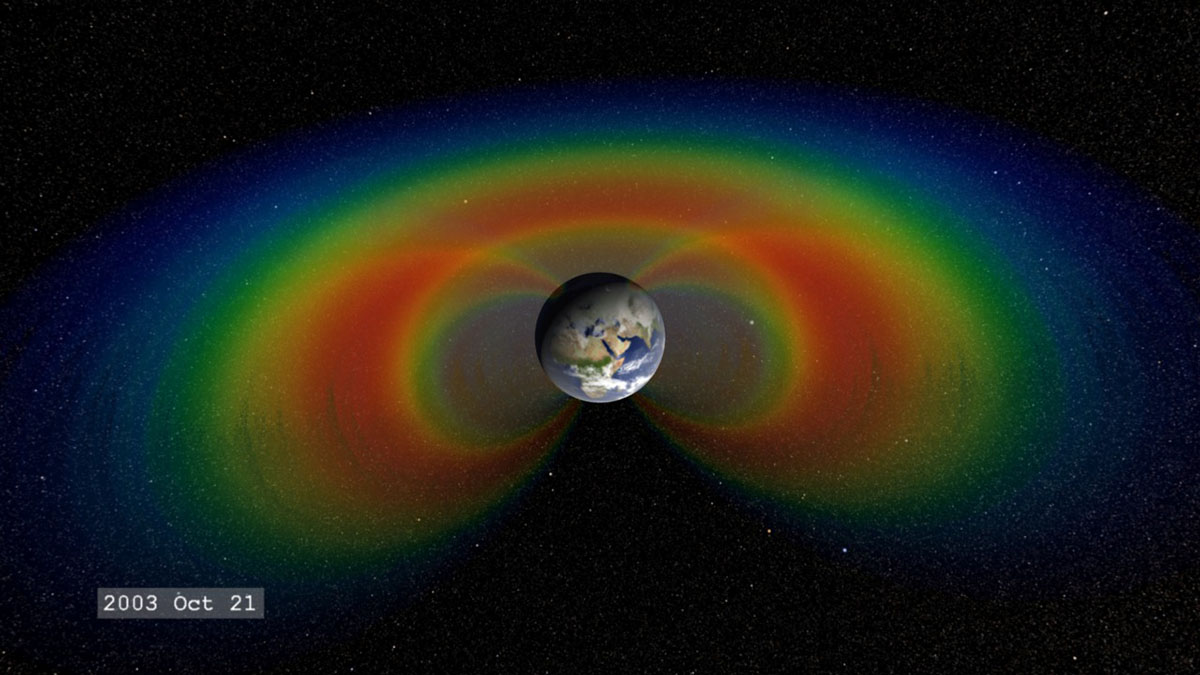
When solar material streams strikes Earth’s magnetosphere, it can become trapped and held in two donut-shaped belts around the planet called the Van Allen Belts. The belts restrain the particles to travel along Earth’s magnetic field lines, continually bouncing back and forth from pole to pole. (NASA Goddard / Tom Bridgman)
Home When solar material streams strikes Earth’s magnetosphere, it can become trapped and held in two donut-shaped belts around the planet called the Van Allen Belts. The belts restrain the particles to travel along Earth’s magnetic field lines, continually bouncing back and forth from pole to pole. (NASA Goddard / Tom Bridgman) When solar material streams strikes Earth’s magnetosphere, it can become trapped and held in two donut-shaped belts around the planet called the Van Allen Belts. The belts restrain the particles to travel along Earth’s magnetic field lines, continually bouncing back and forth from pole to pole. (NASA Goddard / Tom Bridgman)
When solar material streams strikes Earth’s magnetosphere, it can become trapped and held in two donut-shaped belts around the planet called the Van Allen Belts. The belts restrain the particles to travel along Earth’s magnetic field lines, continually bouncing back and forth from pole to pole. (NASA Goddard / Tom Bridgman)