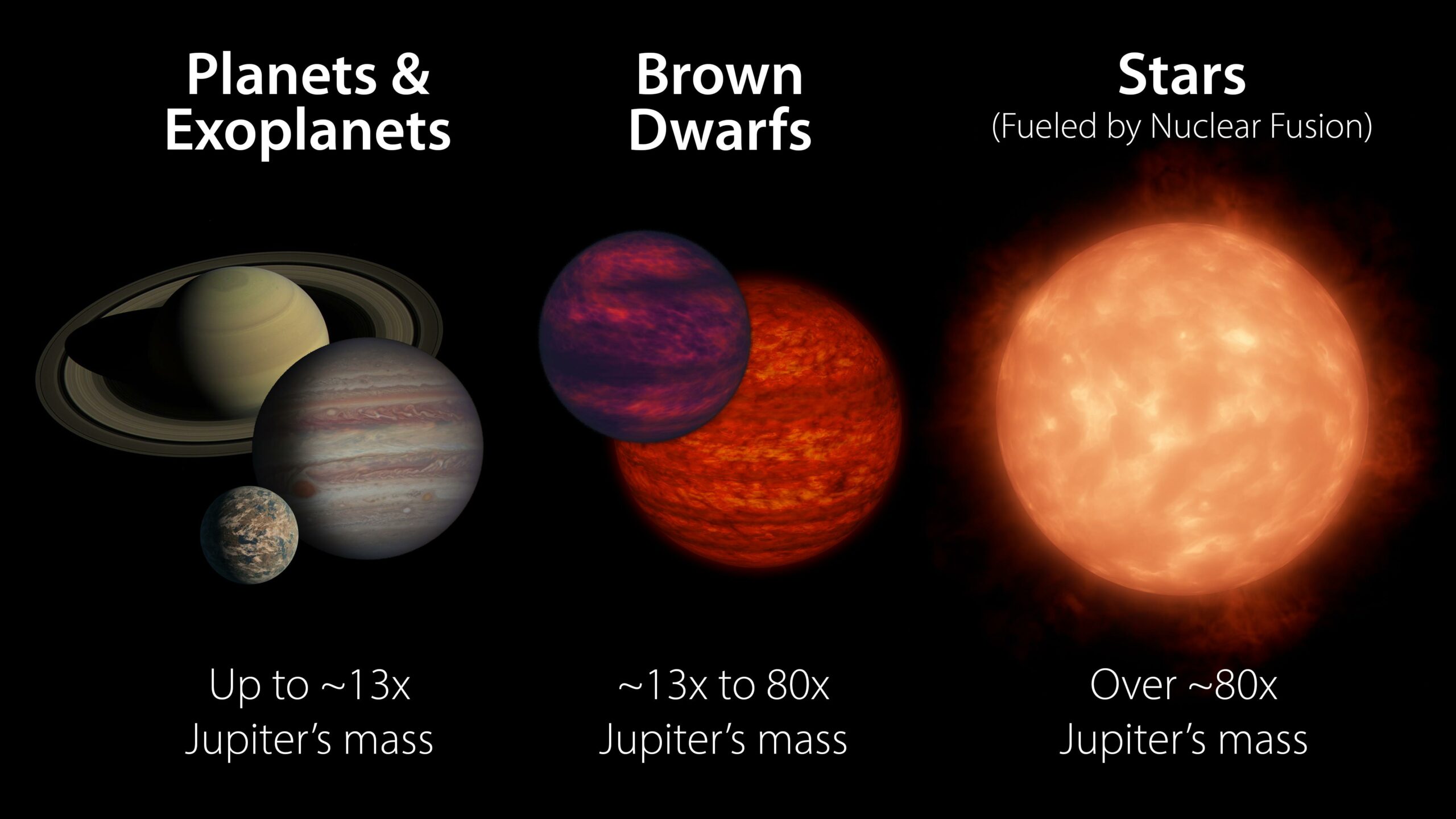
Brown dwarfs are more massive than most planets but not quite as massive as stars. Generally speaking, they have between 13 and 80 times the mass of Jupiter. A brown dwarf becomes a star if its core pressure gets high enough to start nuclear fusion. (NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Home Brown dwarfs are more massive than most planets but not quite as massive as stars. Generally speaking, they have between 13 and 80 times the mass of Jupiter. A brown dwarf becomes a star if its core pressure gets high enough to start nuclear fusion. (NASA/JPL-Caltech) Brown dwarfs are more massive than most planets but not quite as massive as stars. Generally speaking, they have between 13 and 80 times the mass of Jupiter. A brown dwarf becomes a star if its core pressure gets high enough to start nuclear fusion. (NASA/JPL-Caltech)