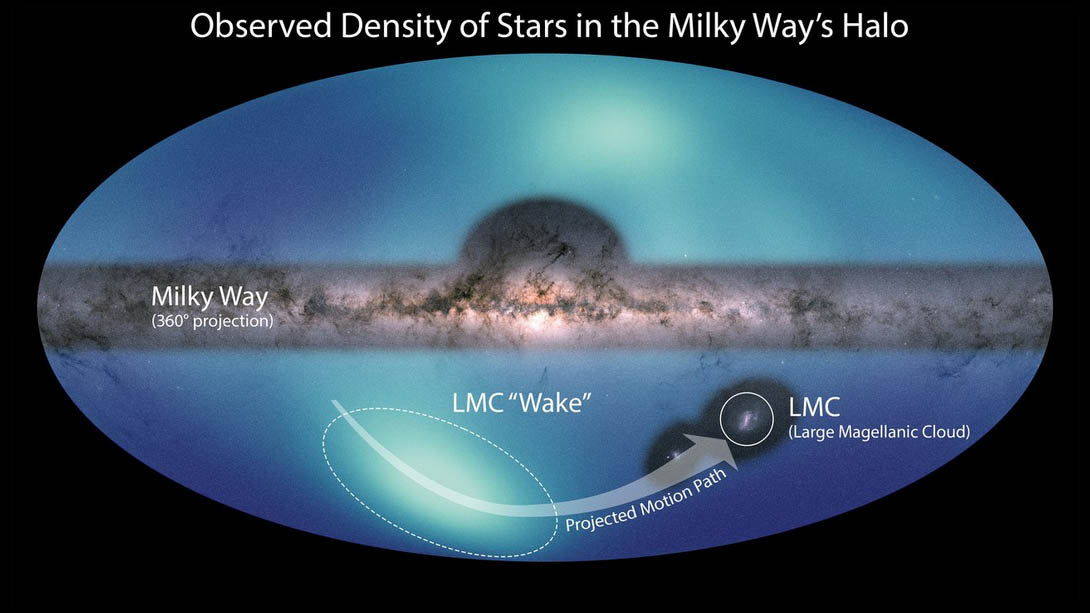
Images of the Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) are overlaid on a map of the surrounding galactic halo. The smaller structure is a wake created by the LMC’s motion through this region. The larger light-blue feature corresponds to a high density of stars observed in the northern hemisphere of our galaxy. (NASA/ESA/JPL-Caltech/Conroy et. al. 2021)
Home Images of the Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) are overlaid on a map of the surrounding galactic halo. The smaller structure is a wake created by the LMC’s motion through this region. The larger light-blue feature corresponds to a high density of stars observed in the northern hemisphere of our galaxy. (NASA/ESA/JPL-Caltech/Conroy et. al. 2021) Images of the Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) are overlaid on a map of the surrounding galactic halo. The smaller structure is a wake created by the LMC’s motion through this region. The larger light-blue feature corresponds to a high density of stars observed in the northern hemisphere of our galaxy. (NASA/ESA/JPL-Caltech/Conroy et. al. 2021)
Images of the Milky Way and the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) are overlaid on a map of the surrounding galactic halo. The smaller structure is a wake created by the LMC’s motion through this region. The larger light-blue feature corresponds to a high density of stars observed in the northern hemisphere of our galaxy. (NASA/ESA/JPL-Caltech/Conroy et. al. 2021)