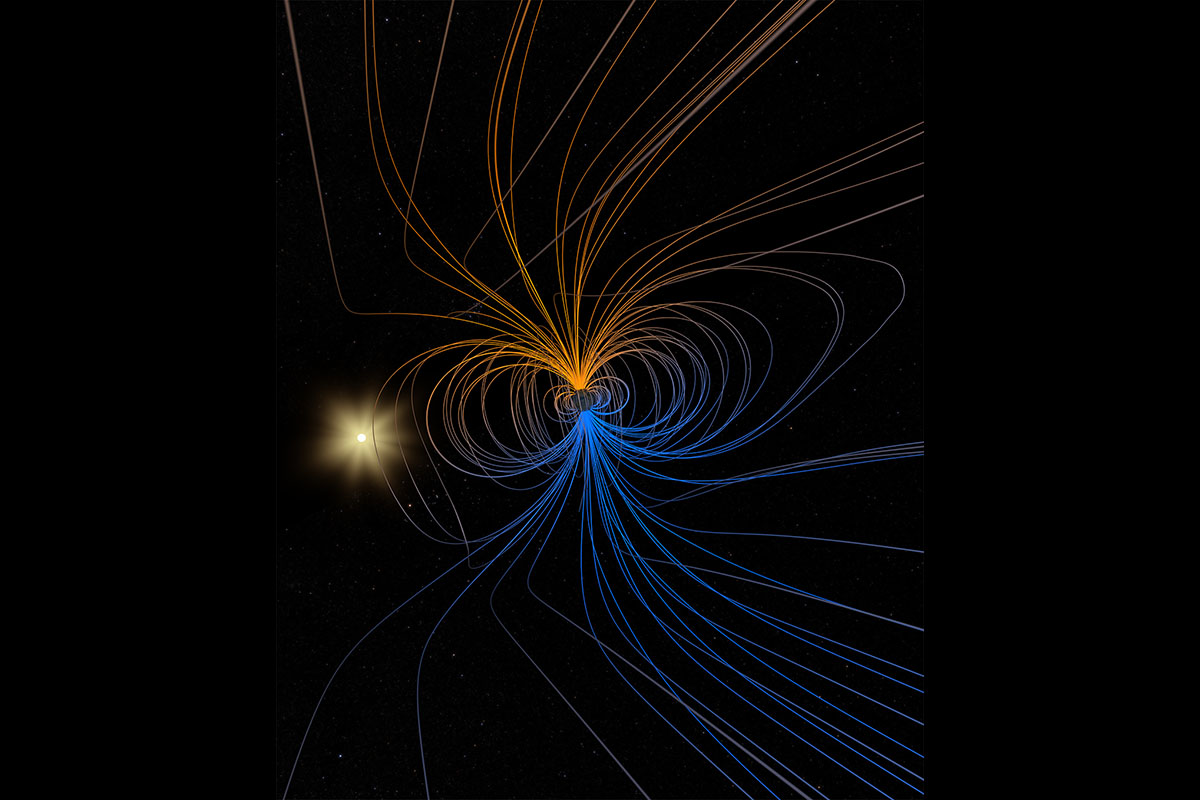
This stereoscopic visualization shows a simple model of the Earth’s magnetic field. The magnetic field partially shields the Earth from harmful charged particles emanating from the Sun. (NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center)
Home This stereoscopic visualization shows a simple model of the Earth’s magnetic field. The magnetic field partially shields the Earth from harmful charged particles emanating from the Sun. (NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center) This stereoscopic visualization shows a simple model of the Earth's magnetic field. The magnetic field partially shields the Earth from harmful charged particles emanating from the Sun. (NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center)