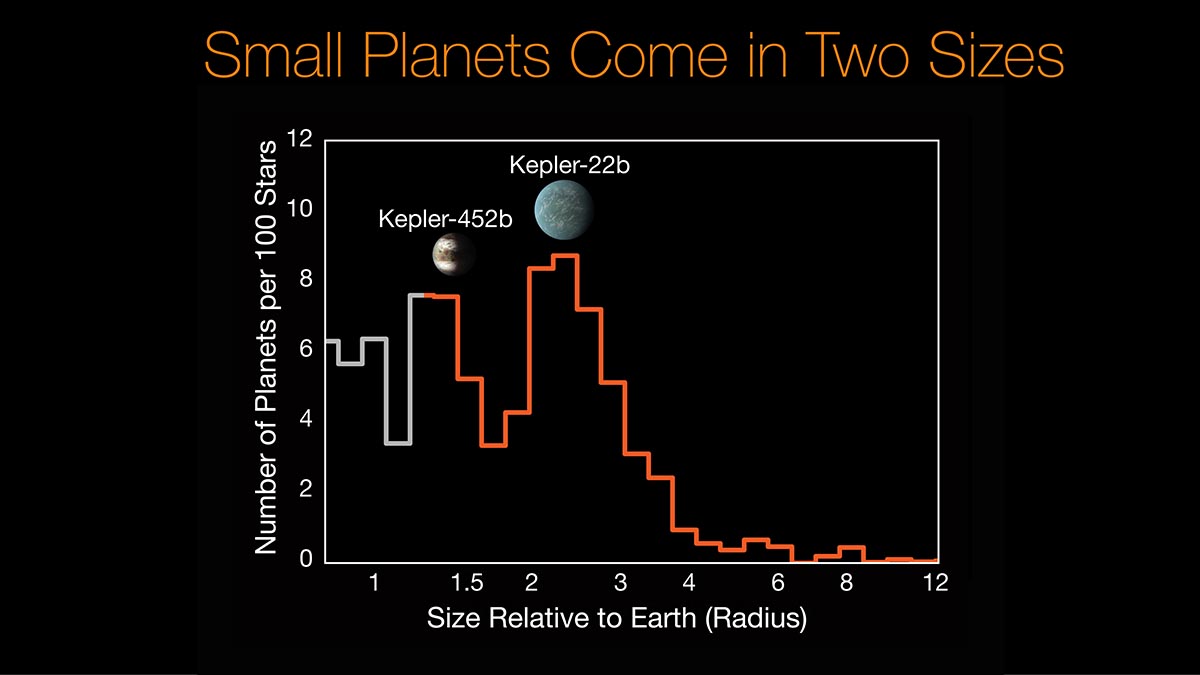
Researchers using data from the W. M. Keck Observatory and NASA’s Kepler mission have discovered a gap in the distribution of planet sizes, indicating that most planets discovered by Kepler so far fall into two distinct size classes: the rocky Earths and super-Earths (similar to Kepler-452b), and the mini-Neptunes (similar to Kepler-22b). (NASA/Ames/Caltech/University of Hawaii (B. J. Fulton))
Home Researchers using data from the W. M. Keck Observatory and NASA’s Kepler mission have discovered a gap in the distribution of planet sizes, indicating that most planets discovered by Kepler so far fall into two distinct size classes: the rocky Earths and super-Earths (similar to Kepler-452b), and the mini-Neptunes (similar to Kepler-22b). (NASA/Ames/Caltech/University of Hawaii (B. J. Fulton)) Researchers using data from the W. M. Keck Observatory and NASA's Kepler mission have discovered a gap in the distribution of planet sizes, indicating that most planets discovered by Kepler so far fall into two distinct size classes: the rocky Earths and super-Earths (similar to Kepler-452b), and the mini-Neptunes (similar to Kepler-22b). (NASA/Ames/Caltech/University of Hawaii (B. J. Fulton))
Researchers using data from the W. M. Keck Observatory and NASA’s Kepler mission have discovered a gap in the distribution of planet sizes, indicating that most planets discovered by Kepler so far fall into two distinct size classes: the rocky Earths and super-Earths (similar to Kepler-452b), and the mini-Neptunes (similar to Kepler-22b). (NASA/Ames/Caltech/University of Hawaii (B. J. Fulton))